CRUD And Search Operation In ASP.NET MVC Application Using Partial View
What is Partial View in ASP.NET MVC?
- Partial view is a view which is rendered in another view
- Partial view render portion of pages
- Using partial view, you can reuse portion of page
- Partial view is similar to a normal view with .cshtml
Project overview
Here I have created an application to keep basic employee information. View, add, update and delete option of an employee is in the application. I used partial view to show employee information in grid. Here I showed how do you run CRUD operation using partial view in most manageable way. Let’s come to the implementation of the project.
Tools and Technology used I used following tools and technology to develop the project –
- Visual Studio 2013
- Visual C#
- ASP.NET MVC 5
- Entity Framework 6
- Razor view engine
- JQuery
Step 1: Create a ASP.net MVC Project
- From Visual studio 2013, choose File->Project -> ASP.NET Web application
- Select MVC Template and click OK
Step 2: Change or Add Connection String
- Change or Add connection string in Web.config as follows
<add name="DefaultConnection" connectionString="Data Source=(LocalDb)\v11.0;AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|\HRMDB.mdf;Initial Catalog=HRMDB;Integrated Security=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
Step 3: Create model classes
Create three model classes Dept, Designation and Employee as follows.
Dept Class
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace Web.HRM.Models
{
public class Dept
{
public Dept()
{
ActionDate = DateTime.Now;
}
[Key, DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Dept")]
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual List<employee> Employees { get; set; }
public DateTime ActionDate { get; set; }
}
}
Designation Class
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace Web.HRM.Models
{
public class Designation
{
public Designation()
{
ActionDate = DateTime.Now;
}
[Key, DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Designation")]
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual List<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
public DateTime ActionDate { get; set; }
}
}
Employee Class
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace Web.HRM.Models
{
public class Employee
{
public Employee()
{
ActionDate = DateTime.Now;
}
[Key, DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Employee Code")]
public string EmpCode { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Full Name")]
public string FullName { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Nick Name")]
public string NickName { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Designation")]
public int DesignationId { get; set; }
[ForeignKey("DesignationId")]
public virtual Designation Designation { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Department")]
public int DeptId { get; set; }
[ForeignKey("DeptId")]
public virtual Dept Dept { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public DateTime ActionDate { get; set; }
}
}
Step 4: Create a Context class
- Create HRMContext Class in Model folder.
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;
using System.Data.Entity;
namespace Web.HRM.Models
{
public class HRMContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser>
{
public HRMContext()
: base("DefaultConnection", throwIfV1Schema: false)
{
}
public static HRMContext Create()
{
return new HRMContext();
}
public DbSet<Dept> Depts { get; set; }
public DbSet<Designation> Designations { get; set; }
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
}
}
Step 5: Create Controller and Views
- Click Right button on Controller Folder->Add Controller.
- Now choose MVC 5 Controller with views, using Entity Framework as scaffolding template.
- Click Add.
- Now select HRMContext as context, Employee as model and type controller name as EmployeeController.
Step 6: Modify the controller
- Modify EmployeeController as follows.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Web.HRM.Models;
namespace Web.HRM.Controllers
{
public class EmployeeController : Controller
{
private HRMContext db = new HRMContext();
// GET: /Employee/
public ActionResult Index()
{
var employees = db.Employees.Include(e => e.Dept).Include(e => e.Designation);
return View(employees.ToList());
}
// GET: /Employee/Details/5
public ActionResult Details(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
Employee employee = db.Employees.Find(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(employee);
}
// GET: /Employee/Create
public ActionResult Create()
{
ViewBag.DeptId = new SelectList(db.Depts, "Id", "Name");
ViewBag.DesignationId = new SelectList(db.Designations, "Id", "Name");
List<Dept> lstDept = db.Depts.ToList();
ViewBag.DeptList = lstDept;
List<Designation> lstDesignation = db.Designations.ToList();
ViewBag.DesignationList = lstDesignation;
return View();
}
// POST: /Employee/Create
// To protect from overposting attacks, please enable the specific properties you want to bind to, for
// more details see http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=317598.
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Create([Bind(Include = "Id,EmpCode,FullName,NickName,DesignationId,DeptId,Phone,Email,Address")] Employee employee)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
employee.ActionDate = DateTime.Now;
if (employee.Id != 0)
db.Entry(employee).State = EntityState.Modified;
else
db.Employees.Add(employee);
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Create");
}
ViewBag.DeptId = new SelectList(db.Depts, "Id", "Name", employee.DeptId);
ViewBag.DesignationId = new SelectList(db.Designations, "Id", "Name", employee.DesignationId);
return View(employee);
}
// GET: /Employee/Edit/5
public ActionResult Edit(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
Employee employee = db.Employees.Find(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
ViewBag.DeptId = new SelectList(db.Depts, "Id", "Name", employee.DeptId);
ViewBag.DesignationId = new SelectList(db.Designations, "Id", "Name", employee.DesignationId);
return View(employee);
}
// POST: /Employee/Edit/5
// To protect from overposting attacks, please enable the specific properties you want to bind to, for
// more details see http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=317598.
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Edit([Bind(Include = "Id,EmpCode,FullName,NickName,DesignationId,DeptId,Phone,Email,Address,ActionDate")] Employee employee)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
db.Entry(employee).State = EntityState.Modified;
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
ViewBag.DeptId = new SelectList(db.Depts, "Id", "Name", employee.DeptId);
ViewBag.DesignationId = new SelectList(db.Designations, "Id", "Name", employee.DesignationId);
return View(employee);
}
// GET: /Employee/Delete/5
public ActionResult Delete(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
Employee employee = db.Employees.Find(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(employee);
}
// POST: /Employee/Delete/5
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id)
{
Employee employee = db.Employees.Find(id);
db.Employees.Remove(employee);
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Create");
//return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
public ActionResult _LoadSearchEmployee(string desigId, string deptId)
{
List<Employee> employee = new List<Employee>();
int _desigId = 0;
int _deptId = 0;
Int32.TryParse(desigId, out _desigId);
Int32.TryParse(deptId, out _deptId);
employee = db.Employees.Where(p => (p.DeptId == _deptId || _deptId == 0) &&
(p.DesignationId == _desigId || _desigId == 0)).ToList();
return PartialView(employee);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
db.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
}
}
Step 7: Create a partial view
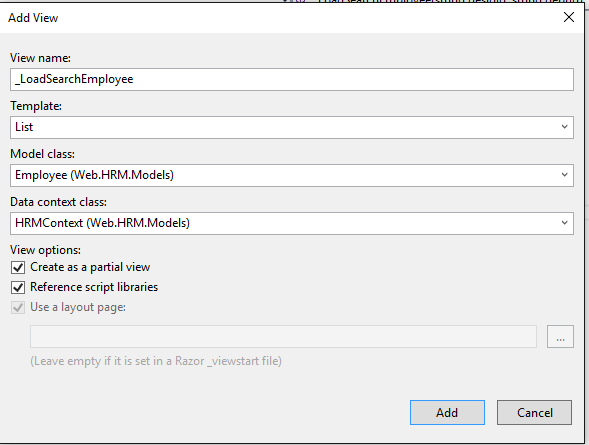
- Create a partial view name _LoadSearchEmployee in Employee Controller.
- Click right button on _LoadSearchEmployee action -> Add View -> Select “Create as a partial view” as follows.
- Modify the partial view “_LoadSearchEmployee” in Views-> Employee folder as follows.
@model IEnumerable<Web.HRM.Models.Employee>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "View1";
}
<h2>List of Employees</h2>
@*<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create")
</p>*@
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.EmpCode)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.FullName)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.NickName)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Designation.Name)
</th>
<th hidden="hidden"></th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Dept.Name)
</th>
<th hidden="hidden"></th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Phone)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Email)
</th>
<th hidden="hidden"></th>
<th hidden="hidden"></th>
<th></th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.EmpCode)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FullName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.NickName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Designation.Name)
</td>
<td hidden="hidden">
@item.DesignationId
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Dept.Name)
</td>
<td hidden="hidden">
@item.DeptId
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Phone)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Email)
</td>
<td hidden="hidden">
@item.Address
</td>
<td hidden="hidden">
@item.Id
</td>
<td>
<input type="button" id="editRow" value="Edit" class="btn btn-link editRow" />
|
@Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id = item.Id }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id = item.Id })
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
<script src="~/Scripts/jquery-1.10.2.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function () {
$('#EmpCode').val('');
$('#FullName').val('');
$('#NickName').val('');
$('#Phone').val('');
$('#Email').val('');
$('.editRow').click(function () {
$('#EmpCode').val($(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(0)').text().trim());
$('#FullName').val($(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(1)').text().trim());
$('#NickName').val($(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(2)').text().trim());
var designationId = $(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(4)').text().trim();
var deptId = $(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(6)').text().trim();
//alert(designationId);
$("#DesignationId").val(designationId);
$("#DeptId").val(deptId);
$('#Phone').val($(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(7)').text().trim());
$('#Email').val($(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(8)').text().trim());
$('#Address').val($(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(9)').text().trim());
var empId = $(this).closest('tr').find('td:eq(10)').text().trim();
//alert(empId);
$("#Id").val(empId);
$("#btnSave").val("Edit");
});
});
</script>
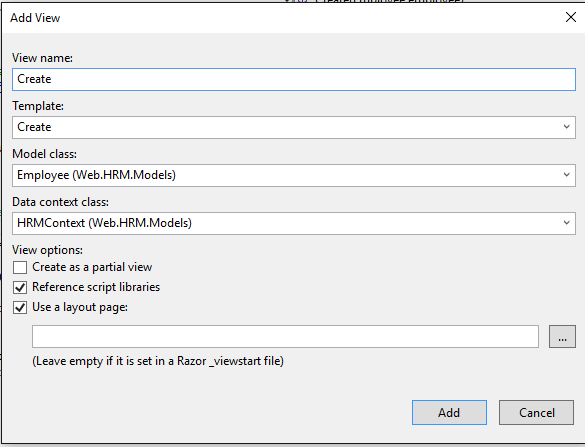
Step 8: Create a View
- Right click on Create action -> Add View name Create as follows.
- Modify the “Create” View and javascript bottom of the view in View->Employee folder as follows.
@model Web.HRM.Models.Employee
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Create";
var lstDept = ViewBag.DeptList;
var lstDesignation = ViewBag.DesignationList;
}
@*<h2>Create</h2>*@
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<h4>Employee Information</h4>
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true)
@*@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.Id)*@
<input type="hidden" value="0" id="Id" name="Id" />
<table>
<tr>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(model => model.EmpCode, new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.EmpCode)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.EmpCode)
</td>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(model => model.FullName, new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.FullName)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.FullName)
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(model => model.NickName, new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.NickName)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.NickName)
</td>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(model => model.DesignationId, "Designation", new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.DropDownList("DesignationId", "---Select Dept---")
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.DesignationId)
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(model => model.DeptId, "Dept", new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.DropDownList("DeptId", "---Select Dept---")
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.DeptId)
</td>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Phone, new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Phone)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Phone)
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Email, new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Email)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Email)
</td>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Address, new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Address)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Address)
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="Save" id="btnSave" class="btn btn-primary" /> ||
@Html.ActionLink("Clear", "Create", "Employee", null, new { @class = "btn btn-primary" })
@*@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")*@
</td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
<hr />
<table>
<tr>
<td>@Html.Label("Dept: ", new { @style = "width : 150px", @class = "control-label col-md-2" }) </td>
<td>
@Html.DropDownList("DeptSearch", new SelectList(lstDept, "Id", "Name"), "---Select Dept---", new { @style = "width : 200px", @class = "form-control" })
</td>
<td>@Html.Label("Designation: ", new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })</td>
<td>
@Html.DropDownList("DesigSearch", new SelectList(lstDesignation, "Id", "Name"), "---Select Designation---", new { @style = "width : 200px", @class = "form-control" })
</td>
<td>
<input type="button" value="Search" class="btn btn-primary" id="getData" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
}
@*<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>*@
<br /><br /><br />
<div id="saveDiv">
@{ Html.RenderAction("_LoadSearchEmployee", new { desigId = "", deptId = "" }); }
</div>
<div id="partial">
</div>
@section Scripts {
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
<script>
$(function () {
$('#getData').click(function () {
//alert('Clicked');
var deptId = $('#DeptSearch').val();
var desigId = $('#DesigSearch').val();
$('#saveDiv').hide();
var url = "@Html.Raw(Url.Action("_LoadSearchEmployee", "Employee", new { desigId = "-parameter", deptId = "sempar" }))";
url = url.replace("-parameter", desigId);
url = url.replace("sempar", deptId);
$('#partial').load(url);
});
});
</script>
}
Step 9: Modify the RouteConfig
- Modify route configuration in App_Start in RouteConfig.cs is as follows. Main reason to modify this class to run the create page by default.
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Routing;
namespace Web.HRM
{
public class RouteConfig
{
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Employee", action = "Create", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
}
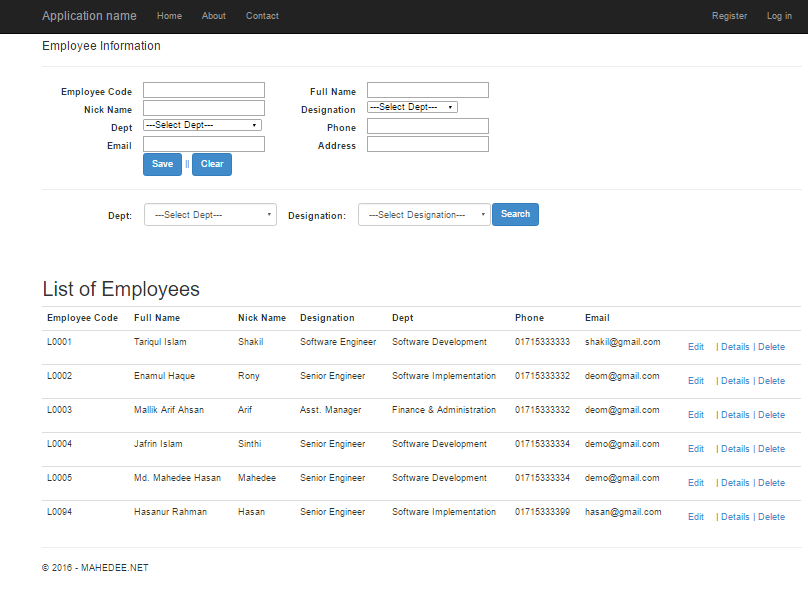
Now run the application, you will see the following output. You can add, view, update and delete employee information in a same page. Thanks for your patience.


Comments