How to Release Port 80: Resolving IIS and Apache/XAMPP Conflicts on Windows
The Problem
When setting up local web development environments on Windows, you might encounter the frustrating “port 80 is busy” or “port already in use” error when trying to start Apache via XAMPP, WAMP, or other web server solutions. This typically occurs because Internet Information Services (IIS) is already running and has claimed port 80, the default HTTP port.
Common Scenarios
This port conflict commonly occurs when:
- Installing XAMPP or WAMP on a Windows machine with IIS enabled
- Switching between development environments (IIS to Apache or vice versa)
- After Windows updates that may re-enable IIS components
- Using multiple web servers for different projects
- Working with containerized applications that need port 80
Error Messages You Might See
12:34:56 PM [Apache] Error: Apache shutdown unexpectedly.
12:34:56 PM [Apache] This may be due to a blocked port, missing dependencies
12:34:56 PM [Apache] Port 80 in use by "Unable to open process" with PID 4!
Understanding Port 80
Port 80 is the standard port for HTTP traffic and can only be used by one service at a time. When multiple web servers attempt to bind to the same port, conflicts arise.
Why This Happens
- IIS starts automatically with Windows if enabled
- System services have priority over user applications
- Windows reserves certain ports for system services
- Only one process can listen on a specific port at a time
Solution 1: Identify What’s Using Port 80
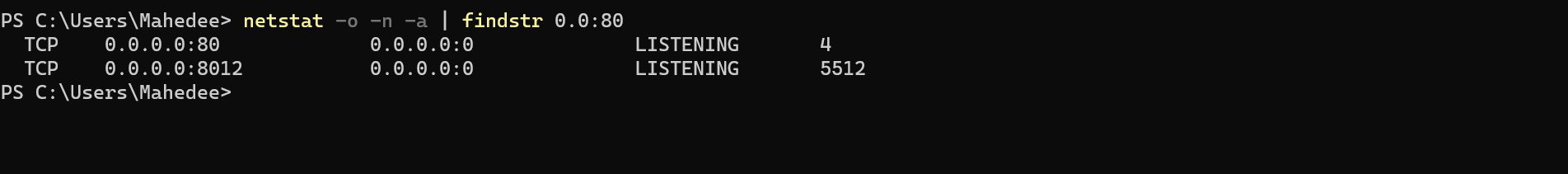
Step 1: Check Port Usage with Netstat
Open Command Prompt as Administrator and run:
netstat -o -n -a | findstr 0.0:80
Alternative modern commands:
# More detailed output
netstat -ano | findstr :80
# PowerShell alternative
Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80
# Using Resource Monitor
resmon.exe
Sample Output:
TCP 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4
TCP [::]:80 [::]:0 LISTENING 4
The last column shows the Process ID (PID). PID 4 typically indicates the Windows System process, often associated with IIS.
Step 2: Identify the Process
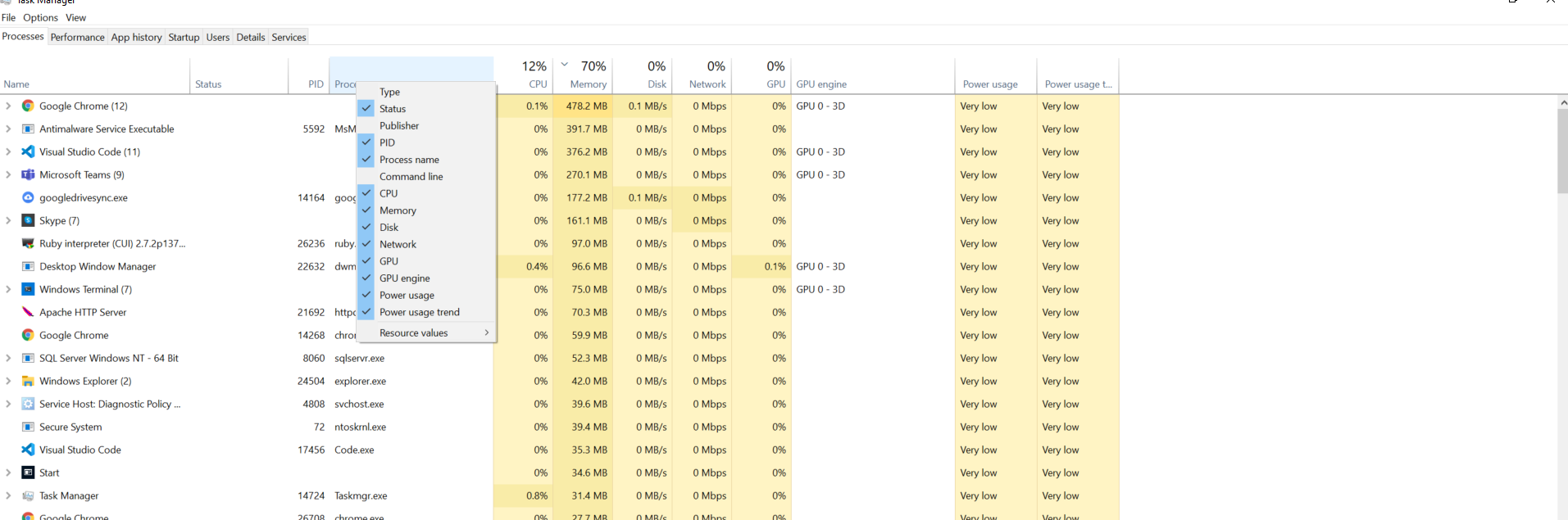
Method 1: Using Task Manager
- Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc)
- Go to the Details tab (or Processes tab in older Windows)
- Click View → Select Columns
- Enable PID (Process Identifier) if not visible
- Find the process with the matching PID
Method 2: Using Command Line
# Find process by PID
tasklist /fi "pid eq 4"
# PowerShell method
Get-Process -Id 4
# More detailed process information
wmic process where processid=4 get name,processid,commandline
Step 3: Identify the Specific Service
If the process is the System process (PID 4), identify which service is using port 80:
# Find which service is using port 80
sc query type= service state= all | findstr /i "iis"
# PowerShell method
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Name -like "*iis*" -or $_.Name -like "*w3*"}
# Check specific IIS services
net start | findstr /i iis
Solution 2: Stop IIS Services
Method 1: Using Services Management Console
- Open Services: Press Win + R, type
services.msc - Find IIS services:
- World Wide Web Publishing Service (W3SVC)
- IIS Admin Service
- Windows Process Activation Service (WAS)
- Right-click each service → Stop
- Set Startup Type to “Manual” or “Disabled” to prevent auto-start
Method 2: Using Command Line
# Stop IIS services
net stop w3svc
net stop iisadmin
net stop was
# PowerShell equivalent
Stop-Service -Name W3SVC, IISADMIN, WAS -Force
# Disable services from starting automatically
sc config w3svc start= disabled
sc config iisadmin start= disabled
sc config was start= disabled
Method 3: Using IIS Manager
# Open IIS Manager
inetmgr.exe
# Or use PowerShell to stop IIS
Import-Module WebAdministration
Stop-Website -Name "Default Web Site"
Solution 3: Configure Alternative Ports
If you need both IIS and Apache running simultaneously:
Configure Apache to Use Different Port
Edit Apache Configuration (usually httpd.conf or in XAMPP: \apache\conf\httpd.conf):
# Change from port 80 to 8080
Listen 80
# Change to:
Listen 8080
# Update ServerName if present
ServerName localhost:8080
Access your site at: http://localhost:8080
Configure IIS to Use Different Port
- Open IIS Manager
- Expand Sites → Default Web Site
- Click Bindings in Actions panel
- Edit HTTP binding to use port 8080
- Save changes
Solution 4: Advanced Troubleshooting
Using Resource Monitor
# Open Resource Monitor
resmon.exe
- Go to Network tab
- Expand Listening Ports
- Find port 80 and identify the process
Using PowerShell for Detailed Analysis
# Get detailed port information
Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80 |
Select-Object LocalAddress, LocalPort, RemoteAddress, RemotePort, State,
@{Name="Process";Expression={(Get-Process -Id $_.OwningProcess).ProcessName}}
# Get IIS application pool information
Import-Module WebAdministration
Get-IISAppPool
Get-IISSite
Using Third-Party Tools
# Using CurrPorts (Nirsoft tool)
cports.exe /scomma ports.csv
# Using TCPView (Microsoft Sysinternals)
tcpview.exe
Solution 5: Windows Features Management
Disable IIS Completely
- Open Control Panel → Programs and Features
- Click “Turn Windows features on or off”
- Uncheck “Internet Information Services”
- Click OK and restart when prompted
PowerShell method:
# Disable IIS feature
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName IIS-WebServerRole
# List all IIS-related features
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online | Where-Object {$_.FeatureName -like "IIS-*"}
Prevention and Best Practices
1. Development Environment Setup
# Create a batch file to quickly stop/start IIS
@echo off
echo Stopping IIS services...
net stop w3svc
net stop iisadmin
echo Starting Apache...
"C:\xampp\apache\bin\httpd.exe" -k start
pause
2. Use Docker for Development
# Dockerfile for isolated Apache environment
FROM httpd:2.4
COPY ./public-html/ /usr/local/apache2/htdocs/
EXPOSE 80
# Docker Compose for multiple services
version: '3'
services:
web:
image: httpd:2.4
ports:
- "8080:80"
volumes:
- ./html:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs/
3. Use Virtual Machines
- VMware Workstation or VirtualBox for isolated environments
- Vagrant for reproducible development setups
- Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2) for Linux-based development
4. Configuration Management
# PowerShell script to switch between IIS and Apache
function Switch-WebServer {
param([string]$Server)
if ($Server -eq "IIS") {
Stop-Service -Name "Apache2.4" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Start-Service -Name "W3SVC", "IISADMIN"
Write-Host "Switched to IIS"
}
elseif ($Server -eq "Apache") {
Stop-Service -Name "W3SVC", "IISADMIN" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Start-Service -Name "Apache2.4"
Write-Host "Switched to Apache"
}
}
# Usage:
# Switch-WebServer -Server "Apache"
# Switch-WebServer -Server "IIS"
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: “Access Denied” When Stopping Services
Solution: Run Command Prompt or PowerShell as Administrator
# Check current privileges
whoami /priv
# Run as administrator
runas /user:Administrator cmd
Issue 2: Services Restart Automatically
Solution: Change service startup type
sc config w3svc start= demand
sc config iisadmin start= demand
Issue 3: Port Still Shows as “In Use”
Solution: Force kill the process
# Find and kill process using port 80
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| findstr :80') do taskkill /f /pid %a
# PowerShell method
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80).OwningProcess | Stop-Process -Force
Issue 4: Multiple Processes Using Port 80
# List all processes using port 80
netstat -ano | findstr :80
# Get detailed information
wmic process where "ProcessId='PID'" get Name,ProcessId,CommandLine
Modern Alternatives and Solutions
1. Using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2)
# Install Apache in WSL2
sudo apt update
sudo apt install apache2
sudo service apache2 start
# Access via localhost from Windows
# WSL2 automatically forwards ports
2. Using Containerization
# docker-compose.yml for development environment
version: '3.8'
services:
web:
image: php:apache
ports:
- "8080:80"
volumes:
- ./src:/var/www/html
database:
image: mysql:8.0
ports:
- "3306:3306"
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: password
3. Using Reverse Proxy
# nginx.conf for reverse proxy setup
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /iis/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080/;
}
location /apache/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8081/;
}
}
Security Considerations
1. Firewall Configuration
# Allow specific port through Windows Firewall
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Apache HTTP" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=8080
# Remove rule
netsh advfirewall firewall delete rule name="Apache HTTP"
2. Service Account Security
# Run services with specific accounts
sc config apache2.4 obj= "NT SERVICE\Apache2.4" password= ""
Conclusion
Port 80 conflicts between IIS and Apache/XAMPP are common in Windows development environments. The key solutions include:
- Identifying the conflicting process using
netstatand Task Manager - Stopping IIS services when not needed
- Configuring alternative ports for one of the services
- Using modern development practices like containers or WSL2
- Implementing automated switching between different web servers
Quick Reference Commands
# Check port 80 usage
netstat -ano | findstr :80
# Stop IIS
net stop w3svc & net stop iisadmin
# Start IIS
net start w3svc & net start iisadmin
# Check service status
sc query w3svc
By following these methods, you can efficiently resolve port conflicts and maintain a smooth development environment. Consider using containerization or virtualization for long-term development environment management to avoid these conflicts entirely.


Comments