Configure service mesh using Istio with an asp.net core applications on Kubernetes
Overview
A service mesh is a configurable infrustructure layer. It have capabilities to handle service-to-service communication, resilency, and many cross-cutting concerns. Proxy is a key component of service mesh. Sidecar proxy is injected in each services in this concept. Here I will show you service mesh communication using Istio with asp.net core applications on Kubernetes environment.
Istio is an open platform for providing a uniform way to integrate microservices, manage traffic flow accross microservices, enforce policies and aggregate telemetry data. Istio uses following tools -
- Prometheus: It monitors everything in the cluster.
- Grafana: Data visualization tools.
- Jaeger: It’s used for distributed tracing.
Tools and Technology used
The following tools and technologies used to configure Istio
- Visual Studio 2022
- Visual C#
- ASP.NET Core Web API
- Ocelot
- Docker desktop
- Kubernetes
- Istio
Let’s configure Istio on asp.net core web api applications.
Step 1: Download Istio
- Go to the link below and download “istio-1.12.2-win.zip”
https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/tag/1.12.2
or download and extract the latest release automatically (Linux or macOS): curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh -
-
Extract zip file and move to the Istio Package directory. For example, istio-1.12.2.
-
Then installation directory contains:
- Sample applications in sample/directory
- The istioctl client binary in the bin/directory
Step 2: Add istioctl client to your path
- Use the following command in git bash to add istioctl client to your path.
export PATH=$PWD/bin:$PATH
Note: The above command doesn’t run on powershell. So, use git bash. If you close the git bash, istioctl doesn’t work. You have to run the above command again.
- To check istioctl client use the following command in git bash.
istioctl
Step 3: Install Istio
- For installation, we use the demo configuration profile. It’s selected to have a good set of defaults for testing, but there are other profiles for production or performance testing. Use below command to install Istio.
istioctl install --set profile=demo -y
- Use the following command to verify Istio.
kubectl get all -n istio-system
Output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/istio-egressgateway-c9cbbd99f-wk265 1/1 Running 0 87s
pod/istio-ingressgateway-7c8bc47b49-xpvvc 1/1 Running 0 86s
pod/istiod-765596f7ff-2p72v 1/1 Running 0 3m13s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/istio-egressgateway ClusterIP 10.101.157.106 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP 85s
service/istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.109.205.109 localhost 15021:32149/TCP,80:30563/TCP,443:30960/TCP,31400:32369/TCP,15443:32309/TCP 85s
service/istiod ClusterIP 10.109.211.149 <none> 15010/TCP,15012/TCP,443/TCP,15014/TCP 3m12s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/istio-egressgateway 1/1 1 1 87s
deployment.apps/istio-ingressgateway 1/1 1 1 86s
deployment.apps/istiod 1/1 1 1 3m13s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/istio-egressgateway-c9cbbd99f 1 1 1 87s
replicaset.apps/istio-ingressgateway-7c8bc47b49 1 1 1 86s
replicaset.apps/istiod-765596f7ff 1 1 1 3m13s
Step 4: Configure for auto proxy injection
- Add a namespace label to instruct Istio to automatically inject Envoy sidecar proxies when you deploy your application later. Use below command to configure default namespance with Istio sidecar proxy.
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
- Check label by using below command
kubectl describe namespace default
Step 5: Create asp.net core applications
- Create 4 asp.net core web api projects.
- Projects names are Catalog.API, Location.API, Ordering.API and BFF.Web.
Step 6: Organize Catalog.API Project
- Add the following nuget packages in the project.
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.InMemory
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
- Add a model class name Product in the model folder.
Product.cs
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace Catalog.API.Model
{
public class Product
{
[Key]
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public int AvailableStock { get; set; }
public int RestockThreshold { get; set; }
}
}
- Add CatalogContext class in Db folder.
CatalogContext.cs
using Catalog.API.Model;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Catalog.API.Db
{
public class CatalogContext : DbContext
{
public CatalogContext(DbContextOptions<CatalogContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder);
}
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
}
}
- Configure InMemory database and modify Program class as follows.
Program.cs
using Catalog.API.Db;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<CatalogContext>(opt => opt.UseInMemoryDatabase("CatalogDB"));
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
- Create ProductsController in Controllers folder
ProductsController.cs
#nullable disable
using Catalog.API.Db;
using Catalog.API.Model;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Catalog.API.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ProductsController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly CatalogContext _context;
public ProductsController(CatalogContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
// GET: api/Products
[HttpGet("GetAll")]
public async Task<ActionResult<IEnumerable<Product>>> GetProducts()
{
return await _context.Products.ToListAsync();
}
// GET: api/Products/5
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Product>> GetProduct(int id)
{
var product = await _context.Products.FindAsync(id);
if (product == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return product;
}
// PUT: api/Products/5
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2123754
[HttpPut("Edit/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> PutProduct(int id, Product product)
{
if (id != product.Id)
{
return BadRequest();
}
_context.Entry(product).State = EntityState.Modified;
try
{
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException)
{
if (!ProductExists(id))
{
return NotFound();
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return NoContent();
}
// POST: api/Products
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2123754
[HttpPost("Add")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Product>> PostProduct(Product product)
{
_context.Products.Add(product);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return CreatedAtAction("GetProduct", new { id = product.Id }, product);
}
// DELETE: api/Products/5
[HttpDelete("Delete/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteProduct(int id)
{
var product = await _context.Products.FindAsync(id);
if (product == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
_context.Products.Remove(product);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return NoContent();
}
private bool ProductExists(int id)
{
return _context.Products.Any(e => e.Id == id);
}
}
}
- Add Dockerfile in the Catalog.API Project
Dockerfile
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:6.0 AS base
WORKDIR /app
EXPOSE 80
EXPOSE 443
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:6.0 AS build
WORKDIR /src
COPY ["/Catalog.API.csproj", "Catalog.API/"]
RUN dotnet restore "Catalog.API/Catalog.API.csproj"
WORKDIR "/src/Catalog.API"
COPY . .
WORKDIR "/src/Catalog.API"
RUN dotnet build "Catalog.API.csproj" -c Release -o /app/build
FROM build AS publish
RUN dotnet publish "Catalog.API.csproj" -c Release -o /app/publish
FROM base AS final
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=publish /app/publish .
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "Catalog.API.dll"]
- Go to director where dockerfile reside and run the following command to build docker image.
docker image build -t mahedee/catalog:1.0.1 .
Note: Don’t forgot to add . at the end of the command.
- To configure pod add the following to file with code in Deploy/k8s folder
deployment.yml
# Configure Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: catalogapi-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: catalogapi-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: catalogapi-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: catalogapi-container
image: mahedee/catalog:1.0.1
resources:
limits:
memory: "128Mi" # 128 mili bytes
cpu: "500m" # 500 mili cpu
ports:
- containerPort: 80
service.yml
# Configure service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: catalogapi-service
spec:
selector:
app: catalogapi-pod
ports:
- port: 8001
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer # use LoadBalancer if you want to accesss out side of pod
- Go to the Deploy/k8s directory and run the following commands.
kubectl apply -f .\deployment.yml
kubectl apply -f .\service.yml
Step 7: Check pods have proxy auto-injected
- By default istio will be injected automatically under this namespace.
- Use the following command to check pods have proxy auto-injected.
kubectl get pods // To check pods
Output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
catalogapi-deployment-68d56ccddd-sqfnj 2/2 Running 0 14m
- Show the catalogapi proxy setup using the following command
kubectl describe pods catalogapi-deployment-68d56ccddd-sqfnj
- Find all proxy container using the following command
docker container ls --filter name=istio-proxy_*
- Check proxy processes for the locationapi
docker container ls --filter name=istio-proxy_catalogapi-deployment* -q
Step 8: Organize Location.API
- Create a Controller name CountriesController in the Controllers folder as follows.
CountriesController.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace Location.API.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class CountriesController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet("GetAll")]
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
return new string[] {"America","Bangladesh", "Canada" };
}
}
}
- Add docker file in the project root directory as follows.
Dockerfile
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:6.0 AS base
WORKDIR /app
EXPOSE 80
EXPOSE 443
ENV ASPNETCORE_URLS=http://*:80;
ENV ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Development
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:6.0 AS build
WORKDIR /src
COPY ["/Location.API.csproj", "Location.API/"]
RUN dotnet restore "Location.API/Location.API.csproj"
WORKDIR "/src/Location.API"
COPY . .
WORKDIR "/src/Location.API"
RUN dotnet build "Location.API.csproj" -c Release -o /app/build
FROM build AS publish
RUN dotnet publish "Location.API.csproj" -c Release -o /app/publish
FROM base AS final
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=publish /app/publish .
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "Location.API.dll"]
- Go to the root directory where Dockerfile reside and run the following command to build docker image.
docker image build -t mahedee/location:1.0.1 .
- To configure pod add the following to file with code in Deploy/k8s folder
deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: locationapi-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: locationapi-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: locationapi-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: locationapi-container
image: mahedee/location:1.0.1
resources:
limits:
memory: "128Mi" # 128 mili bytes
cpu: "500m" # 500 mili cpu
ports:
- containerPort: 80
service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: locationapi-service
spec:
selector:
app: locationapi-pod
ports:
- port: 8002
targetPort: 80
#type: LoadBalancer
- Go to the Deploy/k8s directory and run the following commands.
kubectl apply -f .\deployment.yml
kubectl apply -f .\service.yml
Step 9: Organize Ordering.API
- Add the following nuget packages in the project.
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.InMemory
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
- Create Order class in Models folders as follows.
Order.cs
namespace Ordering.API.Models
{
public class Order
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
public string Comments { get; set; }
}
}
- Create Ordering OrderingContext class in Db folder.
OrderingContext.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Ordering.API.Models;
namespace Ordering.API.Db
{
public class OrderingContext : DbContext
{
public OrderingContext(DbContextOptions<OrderingContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Ordering.API.Models.Order> Order { get; set; }
}
}
- Modify Program.cs to add dbcontext.
Program.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Ordering.API.Db;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<OrderingContext>(opt => opt.UseInMemoryDatabase("CatalogDB"));
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
- Create OrdersController in Controllers folder as follows.
#nullable disable
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Ordering.API.Db;
using Ordering.API.Models;
namespace Ordering.API.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class OrdersController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly OrderingContext _context;
public OrdersController(OrderingContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
// GET: api/Orders
[HttpGet("GetAll")]
public async Task<ActionResult<IEnumerable<Order>>> GetOrder()
{
return await _context.Order.ToListAsync();
}
// GET: api/Orders/5
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Order>> GetOrder(int id)
{
var order = await _context.Order.FindAsync(id);
if (order == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return order;
}
// PUT: api/Orders/5
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2123754
[HttpPut("Edit/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> PutOrder(int id, Order order)
{
if (id != order.Id)
{
return BadRequest();
}
_context.Entry(order).State = EntityState.Modified;
try
{
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException)
{
if (!OrderExists(id))
{
return NotFound();
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return NoContent();
}
// POST: api/Orders
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2123754
[HttpPost("Add")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Order>> PostOrder(Order order)
{
_context.Order.Add(order);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return CreatedAtAction("GetOrder", new { id = order.Id }, order);
}
// DELETE: api/Orders/5
[HttpDelete("Delete/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteOrder(int id)
{
var order = await _context.Order.FindAsync(id);
if (order == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
_context.Order.Remove(order);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return NoContent();
}
private bool OrderExists(int id)
{
return _context.Order.Any(e => e.Id == id);
}
}
}
- Create Docker file in the root directory
Dockerfile
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:6.0 AS base
WORKDIR /app
EXPOSE 80
EXPOSE 443
ENV ASPNETCORE_URLS=http://*:80;
ENV ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Development
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:6.0 AS build
WORKDIR /src
COPY ["/Ordering.API.csproj", "Ordering.API/"]
RUN dotnet restore "Ordering.API/Ordering.API.csproj"
WORKDIR "/src/Ordering.API"
COPY . .
WORKDIR "/src/Ordering.API"
RUN dotnet build "Ordering.API.csproj" -c Release -o /app/build
FROM build AS publish
RUN dotnet publish "Ordering.API.csproj" -c Release -o /app/publish
FROM base AS final
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=publish /app/publish .
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "Ordering.API.dll"]
- Go to the directory where docker file exists and run the following command to build docker image.
docker image build -t mahedee/ordering:1.0.1 .
- To configure pod add the following to file with code in Deploy/k8s folder
deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: locationapi-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: locationapi-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: locationapi-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: locationapi-container
image: mahedee/location:1.0.1
resources:
limits:
memory: "128Mi" # 128 mili bytes
cpu: "500m" # 500 mili cpu
ports:
- containerPort: 80
service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: orderingapi-service
spec:
selector:
app: orderingapi-pod
ports:
- port: 8003
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer
- Go to the Deploy/k8s directory and run the following commands.
kubectl apply -f .\deployment.yml
kubectl apply -f .\service.yml
Step 10: Organize API Gateway BFF.Web
- Install the following nuget packages in the project.
Install-Package Ocelot
Install-Package Ocelot.Cache.CacheManager
- Add ocelot.json file to configure gateway
ocelot.json
{
"Routes": [
//---Catalog service : Start ------------//
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/{url}",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "catalogapi-service",
"Port": 8001
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/Catalog/{url}",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Post", "Put", "Delete" ]
},
//---Catalog service : End ------------//
//---Location Service: Start ----------//
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/{url}",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "locationapi-service",
"Port": 8002
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/Location/{url}",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Post", "Put", "Delete" ]
},
//---Location Service: End ----------//
//---Ordering Service: Start ----------//
// Catch All Routing
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/{url}",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "orderingapi-service",
"Port": 8003
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/Ordering/{url}",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Post", "Put", "Delete" ]
}
],
//---Ordering Service: End ----------//
//https://localhost:7282/api/Products/GetAll
"GlobalConfiguration": {
// enable request correleation id to capture request information
"RequestIdKey": "X-Correlation-Id",
"BaseUrl": "https://localhost:7205/"
}
}
- Modify Program.cs to configure ocelot
Program.cs
using Ocelot.DependencyInjection;
using Ocelot.Middleware;
using Ocelot.Cache.CacheManager;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var environment = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT");
builder.Configuration.SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.AddJsonFile("ocelot.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddEnvironmentVariables();
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
// Swagger for ocelot
//builder.Services.AddSwaggerForOcelot(builder.Configuration);
//builder.Services.AddSwaggerForOcelot();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
//For ocelot
builder.Services.AddOcelot()
// Added for caching
.AddCacheManager(x => {
x.WithDictionaryHandle();
});
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
//app.UseSwaggerForOcelotUI();
}
app.UseOcelot();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
- Add docker file in the root directory.
Dockerfile
#See https://aka.ms/containerfastmode to understand how Visual Studio uses this Dockerfile to build your images for faster debugging.
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:6.0 AS base
WORKDIR /app
EXPOSE 80
EXPOSE 443
ENV ASPNETCORE_URLS=http://*:80;
ENV ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Development
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:6.0 AS build
WORKDIR /src
COPY ["/BFF.Web.csproj", "BFF.Web/"]
RUN dotnet restore "BFF.Web/BFF.Web.csproj"
WORKDIR "/src/BFF.Web"
COPY . .
WORKDIR "/src/BFF.Web"
RUN dotnet build "BFF.Web.csproj" -c Release -o /app/build
FROM build AS publish
RUN dotnet publish "BFF.Web.csproj" -c Release -o /app/publish
FROM base AS final
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=publish /app/publish .
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "BFF.Web.dll"]
- Go to director where dockerfile reside and run the following command to build docker image.
docker image build -t mahedee/bff.web:1.0.1 .
- To configure pod and service add the following yml file with code in Deploy/k8s folder
deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: bffweb-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: bffweb-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: bffweb-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: bffweb-container
image: mahedee/bff.web:1.0.1
resources:
limits:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: bffweb-service
spec:
selector:
app: bffweb-pod
ports:
- port: 8011
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer
- Go to the Deploy/k8s directory and run the following commands.
kubectl apply -f .\deployment.yml
- Now you can running services using in the kubernetes using the following command
kubectl get svc
Output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
bffweb-service LoadBalancer 10.111.186.235 localhost 8011:31690/TCP 10m
catalogapi-service LoadBalancer 10.101.130.94 localhost 8001:30710/TCP 138m
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 3d20h
locationapi-service ClusterIP 10.100.204.33 <none> 8002/TCP 7m57s
orderingapi-service LoadBalancer 10.96.12.11 localhost 8003:31264/TCP 15m
- You can now access catalog api, location api and ordering api using bffweb using the following URL
-
You can use postman for CRUD Operation
http://localhost:8011/Catalog/api/Products/GetAll
http://localhost:8011/Location/api/Countries/GetAll
http://localhost:8011/Ordering/api/Orders/GetAll
Visualizing Service Mesh
Step 11: Install Kiali dashboard
- Go to the Istio’s directory. Install Kiali and other addons and wait for them to be deployed. Execute below command inside Istio folder. Use Git bash instead of powershell.
kubectl apply -f samples/addons
- Execute below command and wait till get success roll out message.
kubectl rollout status deployment/kiali -n istio-system
Note: If there are errors trying to install the addons, try running the command again. There may be some timing issues which will be resolved when the command is run again.
- Verify the deployment with below command.
kubectl get po -n istio-system
Output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
grafana-6ccd56f4b6-sc894 1/1 Running 0 13m
istio-egressgateway-c9cbbd99f-wk265 1/1 Running 0 87m
istio-ingressgateway-7c8bc47b49-xpvvc 1/1 Running 0 87m
istiod-765596f7ff-2p72v 1/1 Running 0 89m
jaeger-5d44bc5c5d-g2wcl 1/1 Running 0 13m
kiali-79b86ff5bc-cqwrp 1/1 Running 0 13m
prometheus-64fd8ccd65-lglld 2/2 Running 0 13m
- Now run the Kiali dashboard using the below command
istioctl dashboard kiali
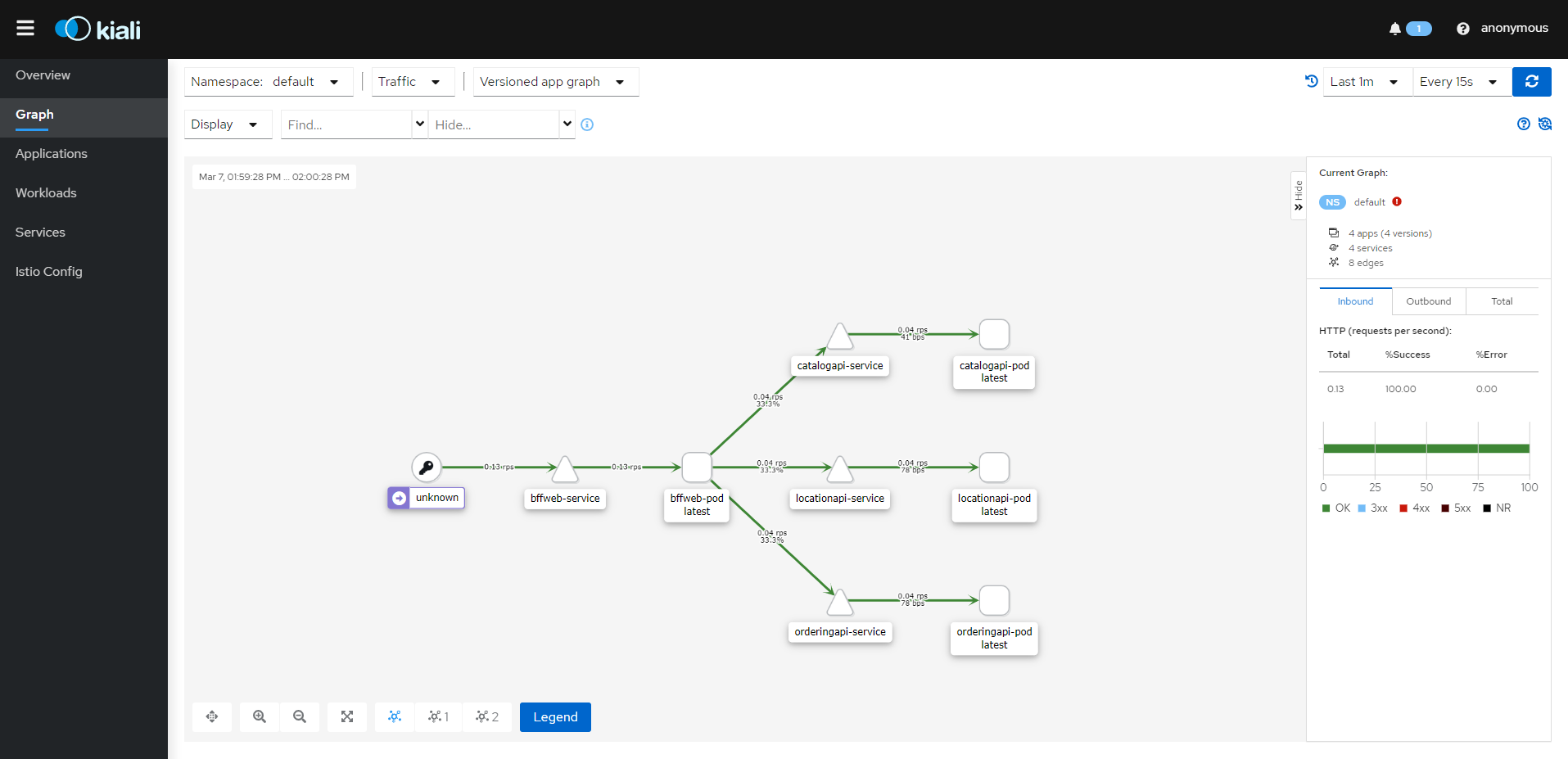
Kiali dashboard will be open. Hit the gateway URL. Use the following URL and hit several times and you will get the reflect in kiali dashbaord as below.
http://localhost:8011/Catalog/api/Products/GetAll
http://localhost:8011/Location/api/Countries/GetAll
http://localhost:8011/Ordering/api/Orders/GetAll
Step 12: Monitoring with Prometheus & Grafana
- Check Prometheus and Grafana is running using the following command.
kubectl get po -n istio-system
- Run Prometheus dashboard using the following command
istioctl dashboard prometheus
View graph in diffrent ways like -
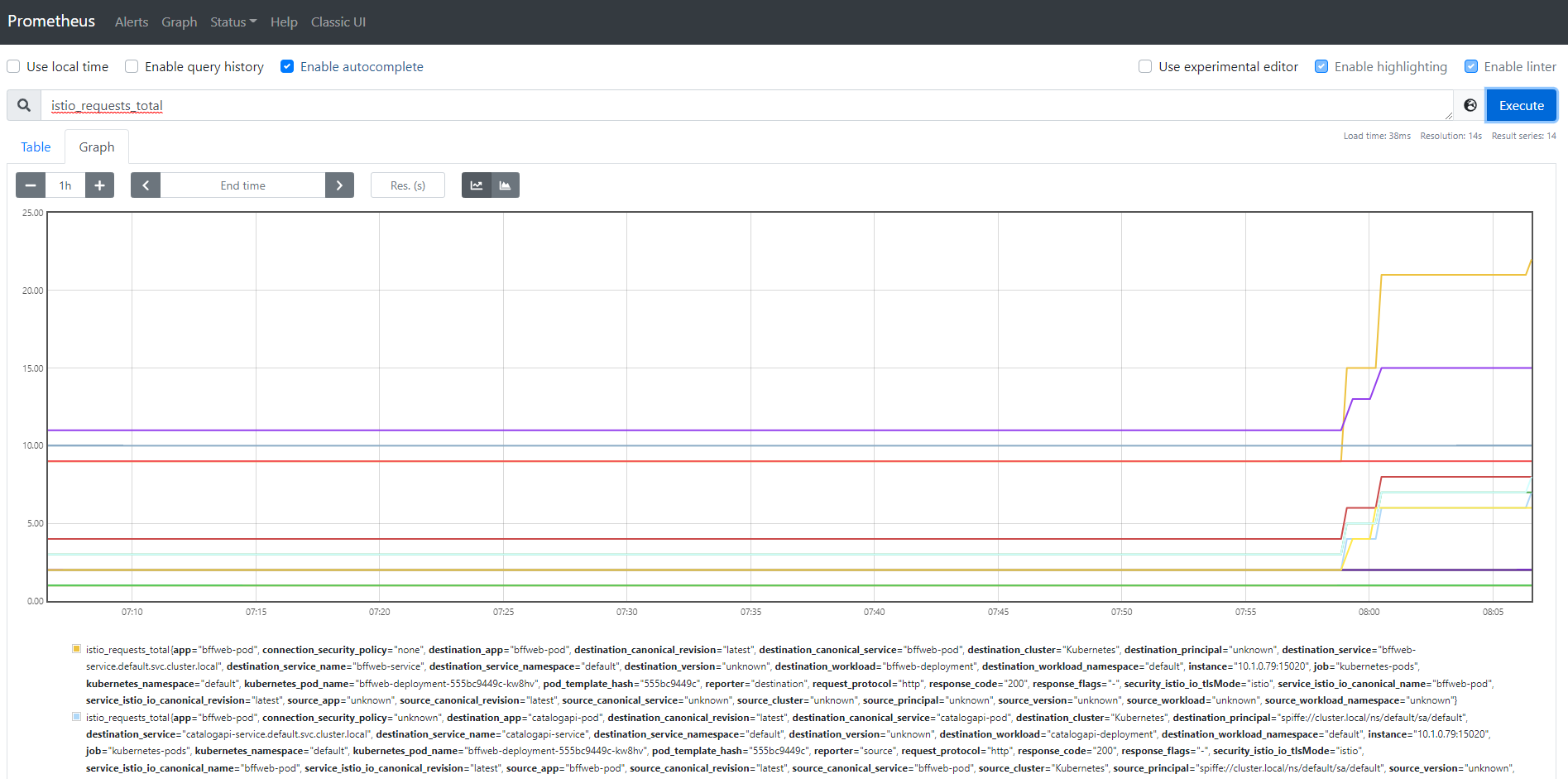
- Select istio_requests_total.
- Switch to Graph.
- Check Status/Targets - Kubernetes service discovery.
- Run Grafana dashboard using the following command
istioctl dashboard grafana
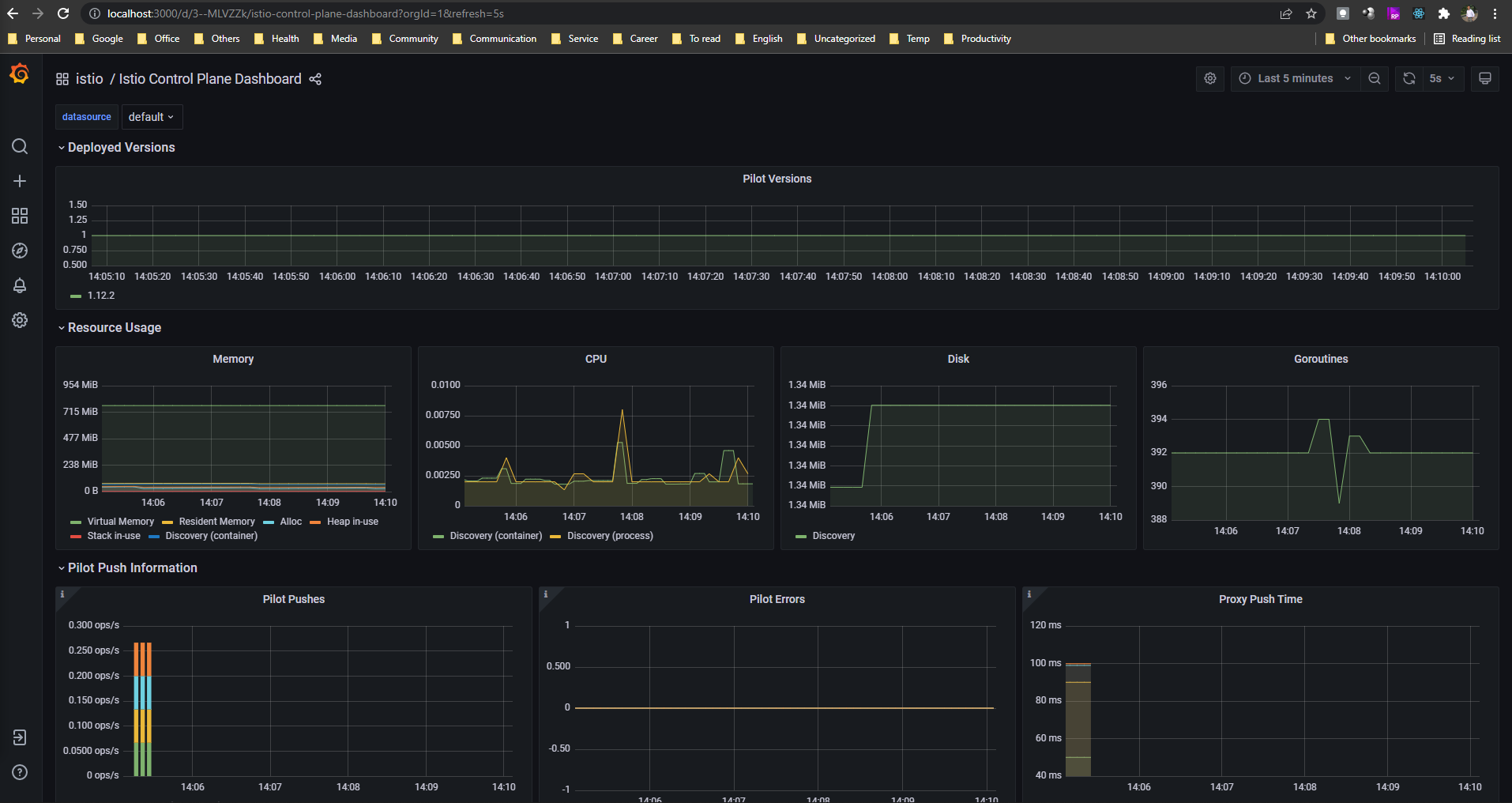
- Go to Dashboar->Manage->Istio and see the dashboar as below.
Step 13: Distributed Tracing using Jaegar UI
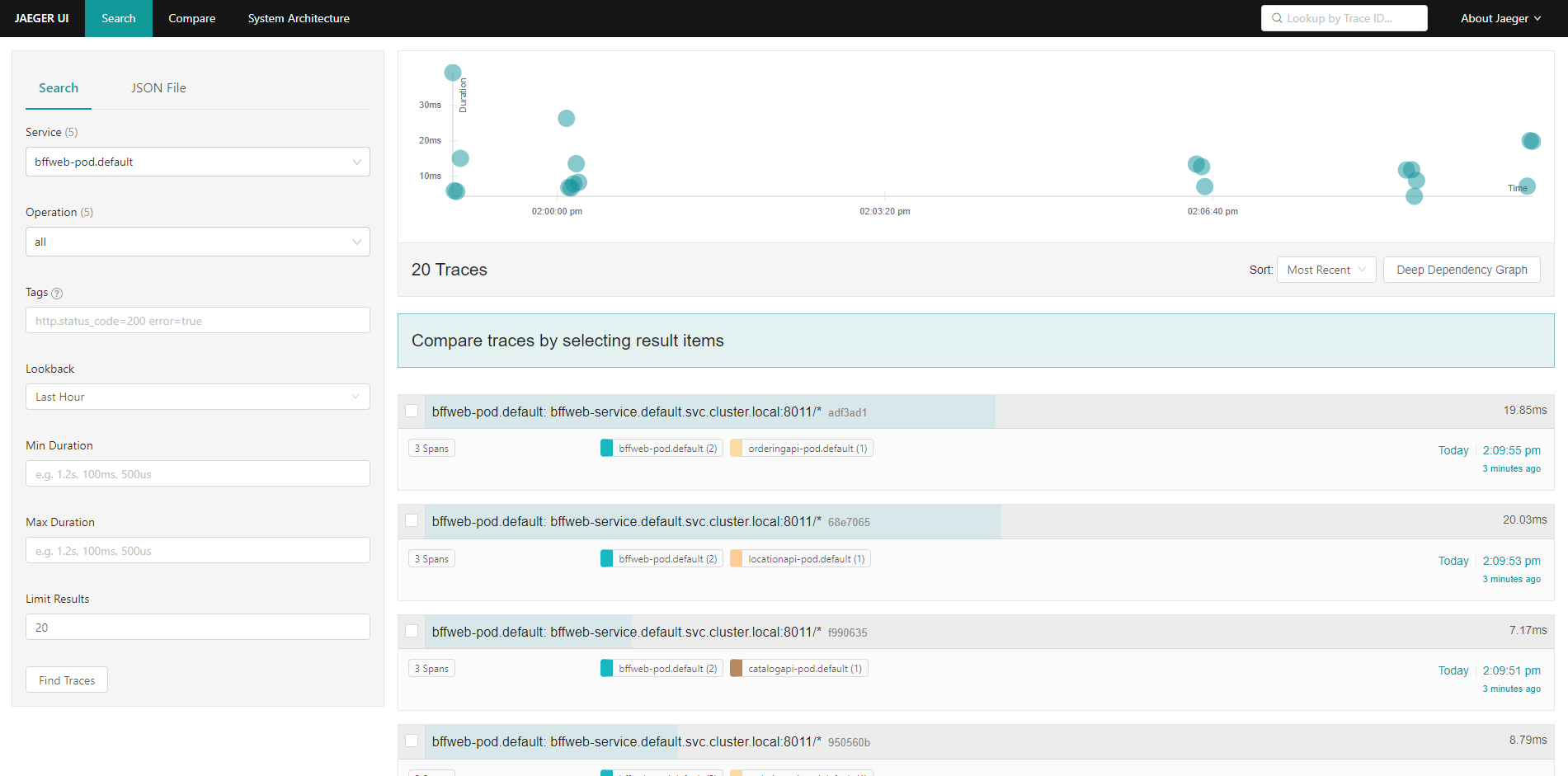
- Run Jaeger UI using the following command
istioctl dashboard jaeger
Step 14: Logging from Istio and Envoy
- Create a YAML file and name the file elasticsearch.yaml and write below code.
elasticsearch.yaml
# Logging Namespace. All below are a part of this namespace.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: logging
---
# Elasticsearch Service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
namespace: logging
labels:
app: elasticsearch
spec:
ports:
- port: 9200
protocol: TCP
targetPort: db
selector:
app: elasticsearch
---
# Elasticsearch Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
namespace: logging
labels:
app: elasticsearch
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: elasticsearch
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: elasticsearch
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
containers:
- image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss:6.1.1
name: elasticsearch
resources:
# need more cpu upon initialization, therefore burstable class
limits:
cpu: 1000m
requests:
cpu: 100m
env:
- name: discovery.type
value: single-node
ports:
- containerPort: 9200
name: db
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 9300
name: transport
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- name: elasticsearch
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: elasticsearch
emptyDir: {}
- Create a YAML file and name the file kibana.yaml and write below code.
kibana.yaml
# Kibana Service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kibana
namespace: logging
labels:
app: kibana
spec:
ports:
- port: 5601
protocol: TCP
targetPort: ui
selector:
app: kibana
---
# Kibana Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kibana
namespace: logging
labels:
app: kibana
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kibana
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kibana
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
containers:
- name: kibana
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana-oss:6.1.1
resources:
# need more cpu upon initialization, therefore burstable class
limits:
cpu: 1000m
requests:
cpu: 100m
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_URL
value: http://elasticsearch:9200
ports:
- containerPort: 5601
name: ui
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: kibana-gateway
namespace: logging
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- port:
number: 15033
name: http-kibana
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: kibana-vs
namespace: logging
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- kibana-gateway
http:
- match:
- port: 15033
route:
- destination:
host: kibana
port:
number: 5601
- Create a YAML file and name the file fluentd.yaml and write below code.
fluentd.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: kube-system
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: fluentd
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: fluentd
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: fluentd
namespace: kube-system
---
# Fluentd Service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fluentd-es
namespace: kube-system
labels:
app: fluentd-es
spec:
ports:
- name: fluentd-tcp
port: 24224
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 24224
- name: fluentd-udp
port: 24224
protocol: UDP
targetPort: 24224
selector:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
version: v1
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
version: v1
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
spec:
serviceAccount: fluentd
serviceAccountName: fluentd
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
containers:
- name: fluentd
image: fluent/fluentd-kubernetes-daemonset:v1.3-debian-elasticsearch
env:
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_HOST
value: "elasticsearch.logging"
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_PORT
value: "9200"
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_SCHEME
value: "http"
- name: FLUENT_UID
value: "0"
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
- Now execute all above file with below commands.
kubectl apply -f elasticsearch.yaml
kubectl apply -f kibana.yaml
kubectl apply -f fluentd.yaml
kubectl get pods -n logging
- If you are using docker desktop you can use below command to port forward.
kubectl port-forward svc/kibana 8099:5601 -n logging
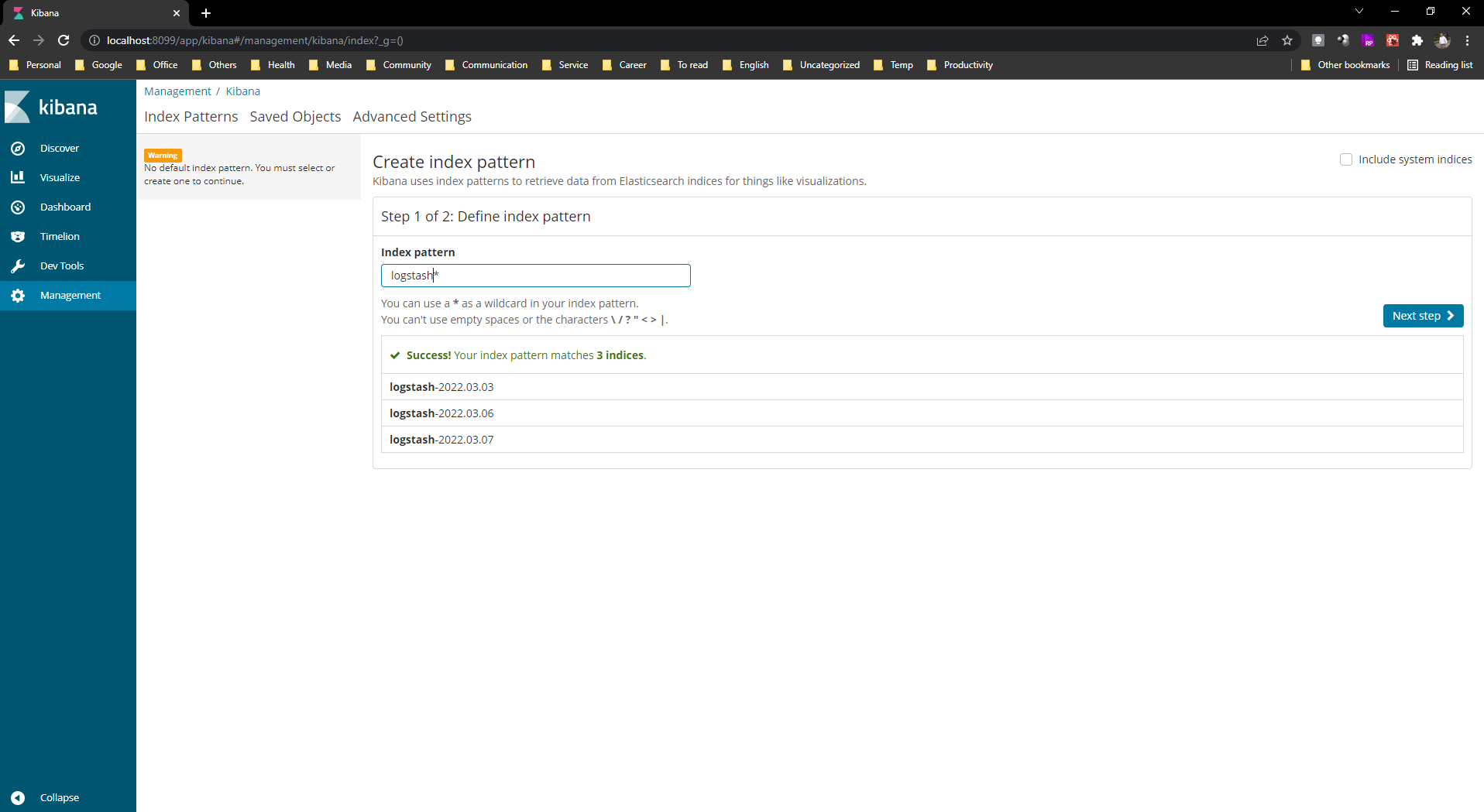
- Now browse kibana using http://localhost:8099/
Step 15: Configure Istio to Log to Fluentd
Now we are going to configure Istio to use the same FluentD instance, and send proxy logs through FluentD into Elasticsearch. It will be actual adapter configuration that I mentioned earler.
- Create a YAMl file and name the file fluentd-istio.yaml and write below code.
fluentd-istio.yaml
# Configuration for logentry instances
apiVersion: config.istio.io/v1alpha2
kind: instance
metadata:
name: newlog
namespace: istio-system
spec:
compiledTemplate: logentry
params:
severity: '"info"'
timestamp: request.time
variables:
source: source.labels["app"] | source.workload.name | "unknown"
user: source.user | "unknown"
destination: destination.labels["app"] | destination.workload.name | "unknown"
responseCode: response.code | 0
responseSize: response.size | 0
latency: response.duration | "0ms"
monitored_resource_type: '"UNSPECIFIED"'
---
# Configuration for a Fluentd handler
apiVersion: config.istio.io/v1alpha2
kind: handler
metadata:
name: handler
namespace: istio-system
spec:
compiledAdapter: fluentd
params:
address: "fluentd-es.kube-system:24224"
---
# Rule to send logentry instances to the Fluentd handler
apiVersion: config.istio.io/v1alpha2
kind: rule
metadata:
name: newlogtofluentd
namespace: istio-system
spec:
match: "true" # match for all requests
actions:
- handler: handler
instances:
- newlog
---
- Apply the below command
kubectl apply -f fluentd-istio.yaml
- Filter on search with kubernetes.container.name is istio-proxy and we will see logs fron istio proxy.
Some commands you may need
Kubectl Commands
kubectl get ns // Get all namesapces
kubectl get svc -n istio-system // Get services under istio-system name space
kubectl get all -n istio-system // Get all under istio-system name space
kubectl delete ns istio-system // Delete namespace name istio-system
kubectl get all // Get everything in the kubernetes
kubectl delete --all pods // Delete all pods
kubectl delete --all pods --namespace=foo // Delete all pods under the namespace foo
kubectl delete --all deployments --namespace=foo // Delete all deployments under the namespace foo
kubectl delete --all namespaces // Delete all name spaces
kubectl delete --all svc // Delete all services
kubectl delete --all deployments // Delete all deployments
Docker Commands
docker rm -vf $(docker ps -aq) // To delete all containers including its volumes use
docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq) // To delete all the images
docker images // To check docker images
docker image build -t mahedee/location:1.0.1 . // create a docker image name mahedee/location:1.0.1

Comments